Compact Laser Ignition for Vacuum Arc Thrusters
Conference Poster - IEPC 2025, UniBw
A novel ignition method for Vacuum Arc Thrusters was demonstrated of a compact laser ignition system based on laser diodes. A pulsed laser driver was developed to generate adjustable pulses. Microsecond laser pulses were focused onto candidate ablation materials biased by a pulse-forming network, where laser-induced ablation initiated the arc discharge. Experiments demonstrated successful ignition with pyrolytic carbon and graphite. By introducing a nearby flow path, the initial seed arc was elongated and transferred to a secondary material, where the main discharge occurred. This effectively decouples the ignition process from the electrode erosion. These results mark a pivotal step toward the development of VATs fully reliant on laser ignition.
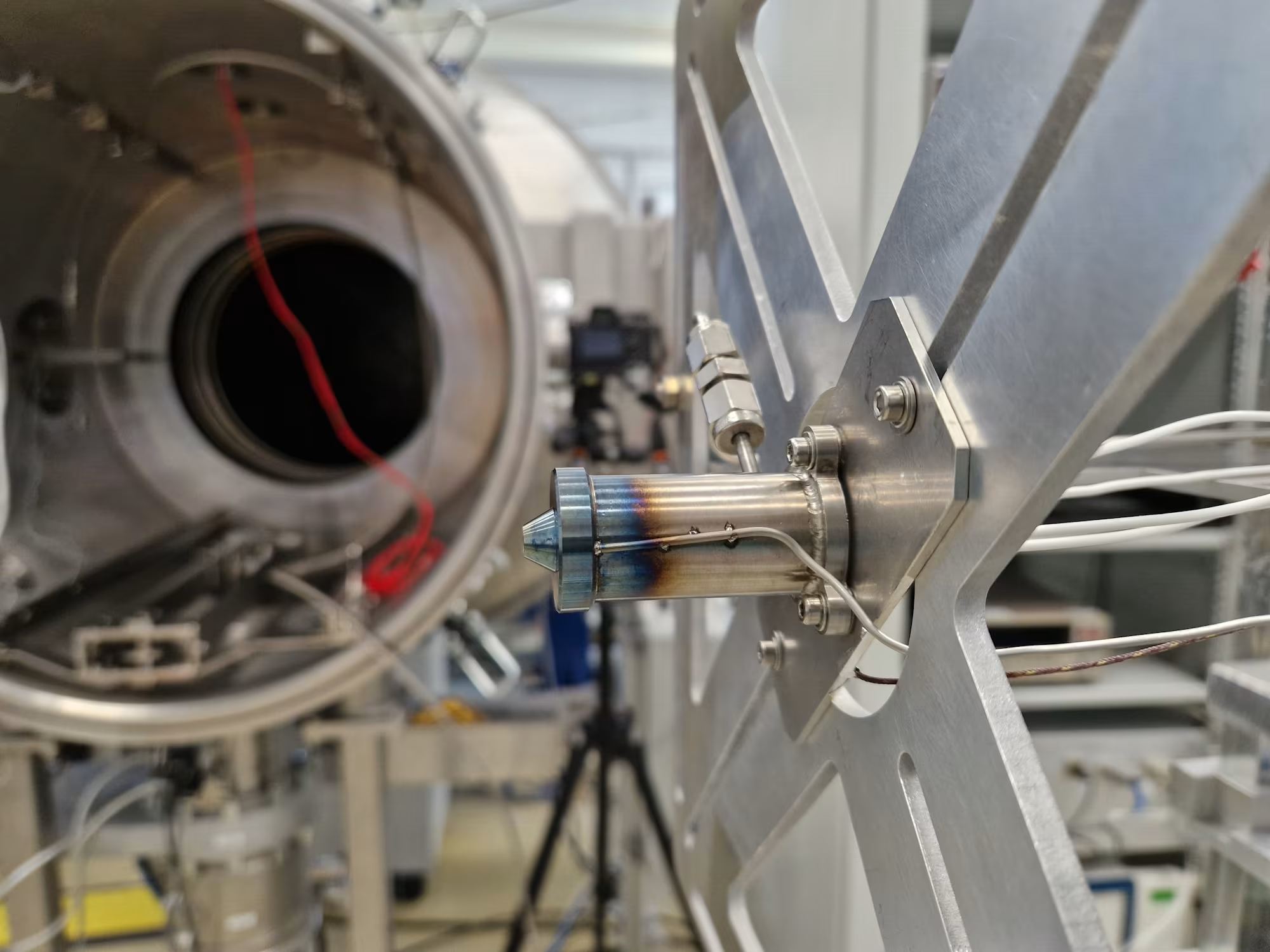
Experimental Characterisation of the XR-100 Resistojet in the ESA Propulsion Laboratory
Masterthesis - 2024, ESA & TUM
An experimental setup was constructed and executed at ESTEC, the Netherlands. Multiple data acquisition systems based on LabVIEW were used to record key parameters during testing. The Imperial College London thrust balance was utilised and improved in several aspects. The calibration procedure and evaluation were automated, the uncertainty budget was expanded, and a new post-processing method was developed to support thrust curve measurements. Uncertainty budgets were determined for the mass flow rate and thrust measurements, and propagated to the resulting specific impulse. This characterisation served to develop comprehensive skills related to vacuum testing of electric propulsion systems.
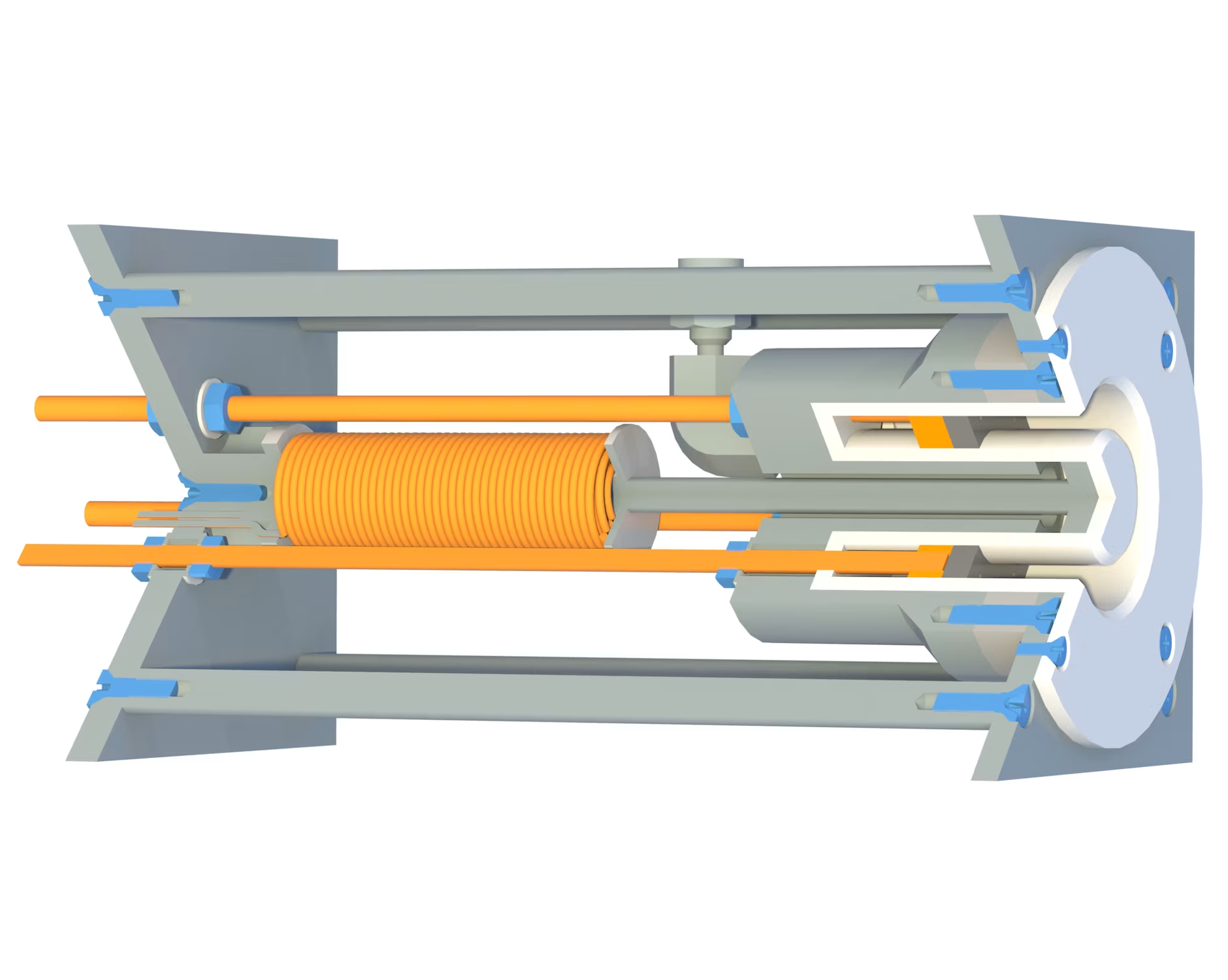
Design of a Hall Thruster and Investigation for a Water Electrolysis Propulsion System
Semesterthesis - 2024, TUM
As an early stage investigation on electrical propulsion via electrolysis, a Hall Thruster was designed for operation on molecular oxygen. A magnetically shielded configuration was developed through simulations with FEMM. To enable parametric testing, the discharge channel length was layed out to be stepless adjustable. Nevertheless, it is concluded that electric propulsion based on oxygen is facing drawbacks in low efficiency, especially when evaluated over the full electrolysis system. As alternative, experimental ideas for OH- ion extraction directly from the water are proposed.
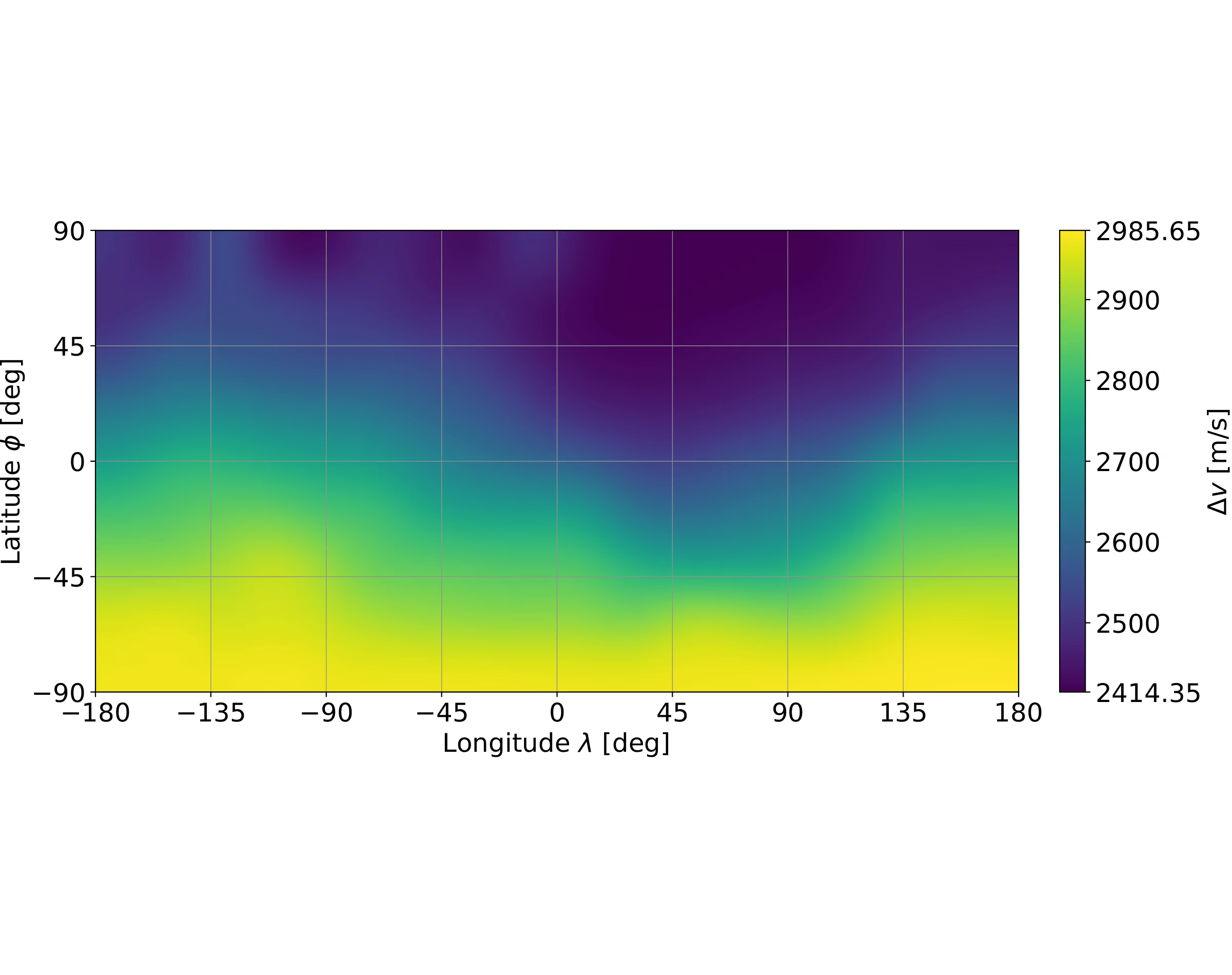
Location-dependent flight cost difference from the lunar surface to an orbital fuel depot and its influence on in-situ resource utilisation location selection
Peer Reviewed Research Paper - 2024, DLR
In order to determine the most optimal location for a robotic factory on the moon, production- and transportation dependencies have been compared. In this work, the process of ilmenite reduction was analysed globally with imaging data of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and factory scaling models. For the transportation costs a global delta-v map to the 9:2 NRHO was constructed, which was applied to a launcher. The key finding is an insignificant influence of the transportation costs on the location selection.





